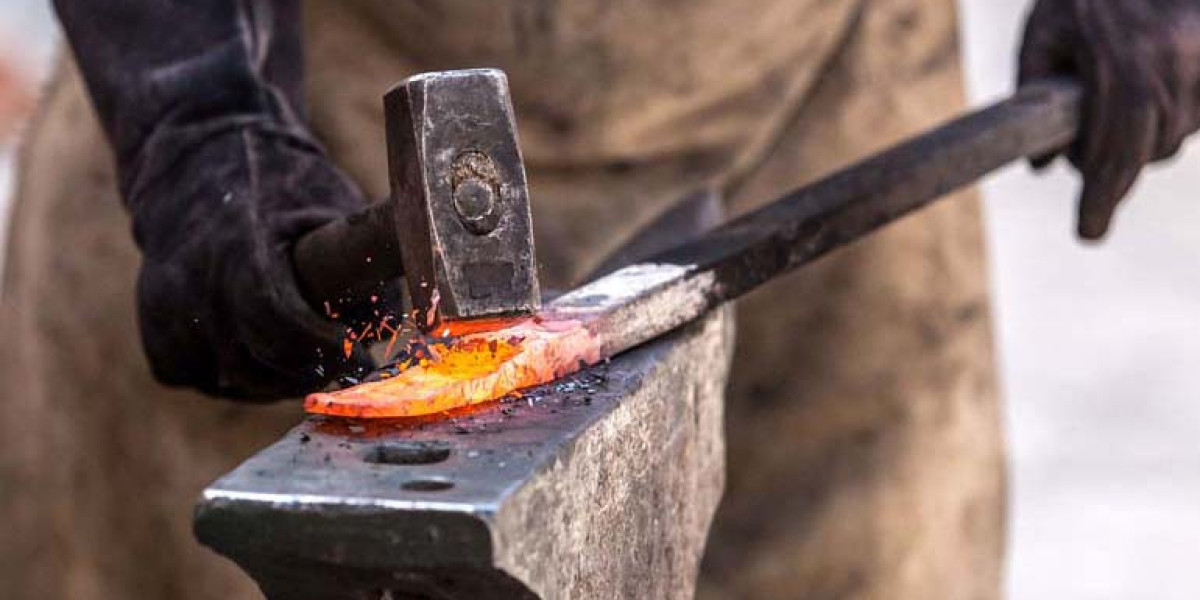
Welcome to the world of fabrication and welding, where metal meets innovation and craftsmanship shapes the future. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate world of fabrication and welding, exploring its Fabrication & Welding significance across various industries, the diverse processes involved, safety precautions, career prospects, and much more.
Importance of Fabrication & Welding in Various Industries
Fabrication and welding play a pivotal role in numerous sectors, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. These processes are the backbone of infrastructure development, vehicle production, and the creation of intricate machinery. Without fabrication and welding, the modern world as we know it would cease to exist.
Types of Fabrication Processes
Welding
Welding is the process of joining two or more metal pieces by melting them together. It's a fundamental technique in fabrication, enabling the creation of sturdy and durable structures.
Cutting
Cutting involves the removal of excess material from a workpiece to achieve the desired shape and size. Various methods such as laser cutting, plasma cutting, and waterjet cutting are employed in fabrication.
Forming
Forming refers to the shaping of metal sheets or plates into specific configurations. Techniques like bending, rolling, and stamping are commonly used in fabrication to mold metal according to design requirements.
Machining
Machining involves the removal of material through cutting, drilling, milling, or turning to create precise components. It's an essential process in fabrication for achieving intricate designs and tight tolerances.
Welding Techniques
Arc Welding
Arc welding uses an electric arc to generate heat and melt the base metals, forming a weld pool. This technique is versatile and suitable for various materials, including steel, aluminum, and titanium.
MIG Welding
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding utilizes a wire electrode fed through a welding gun, which melts and fuses with the base metal to create the weld. It's commonly used in automotive and manufacturing industries for its efficiency and ease of use.
TIG Welding
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. It offers precise control over the welding process and is ideal for welding thin materials and exotic metals.
Resistance Welding
Resistance welding relies on the application of pressure and electrical resistance to join metals. It's widely used in mass production applications, such as automotive assembly lines and appliance manufacturing.
Materials Used in Fabrication & Welding
Fabrication and welding involve working with various materials, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and alloys. Each material has its unique properties and applications, requiring different welding techniques and processes.
Safety Measures in Fabrication & Welding
Safety is paramount in fabrication and welding due to the inherent risks associated with working with high temperatures, heavy machinery, and hazardous materials. Proper training, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to safety protocols are essential to prevent accidents and injuries.
Advantages of Fabrication & Welding
Fabrication and welding offer numerous advantages, including:
- Customization: Ability to create tailor-made components according to specific requirements.
- Strength and Durability: Welded structures are robust and capable of withstanding heavy loads and harsh environments.
- Cost-effectiveness: Fabrication and welding processes optimize material usage and minimize production costs.
- Versatility: Wide range of materials and techniques available to meet diverse needs and applications.
Challenges and Risks in Fabrication & Welding
Despite its benefits, fabrication and welding pose several challenges and risks, such as:
- Welding Defects: Issues like porosity, cracking, and distortion can compromise the integrity of welded joints.
- Occupational Hazards: Exposure to fumes, radiation, and noise can pose health risks to workers if proper precautions are not taken.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistency and precision in fabrication processes requires rigorous quality control measures.
Future Trends in Fabrication & Welding Technology
The future of fabrication and welding is marked by advancements in automation, robotics, and digitalization. Technologies like 3D printing, laser welding, and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing the industry, offering faster production times, enhanced precision, and greater efficiency.
Career Opportunities in Fabrication & Welding
The field of fabrication and welding offers a wide range of career opportunities, including:
- Welding Technician
- Fabrication Engineer
- Quality Control Inspector
- Welding Instructor
- Metal Fabricator
With the growing demand for skilled professionals in manufacturing and construction sectors, pursuing a career in fabrication and welding can Fabrication & Welding lead to rewarding and fulfilling employment prospects.
Conclusion
Fabrication and welding are the cornerstone of modern industries, driving innovation, infrastructure development, and economic growth. From skyscrapers to spacecraft, these processes shape the world around us, creating structures and machinery that propel society forward. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the techniques and applications of fabrication and welding, ensuring a dynamic and vibrant future for this indispensable industry.