As the global population ages, the healthcare industry faces new challenges in addressing the unique needs of seniors. One often overlooked aspect of aging is oral health, which significantly impacts overall well-being. Traditional dental implants may pose limitations for seniors with bone loss, making zygomatic implants an innovative solution that redefines oral health in the aging population.
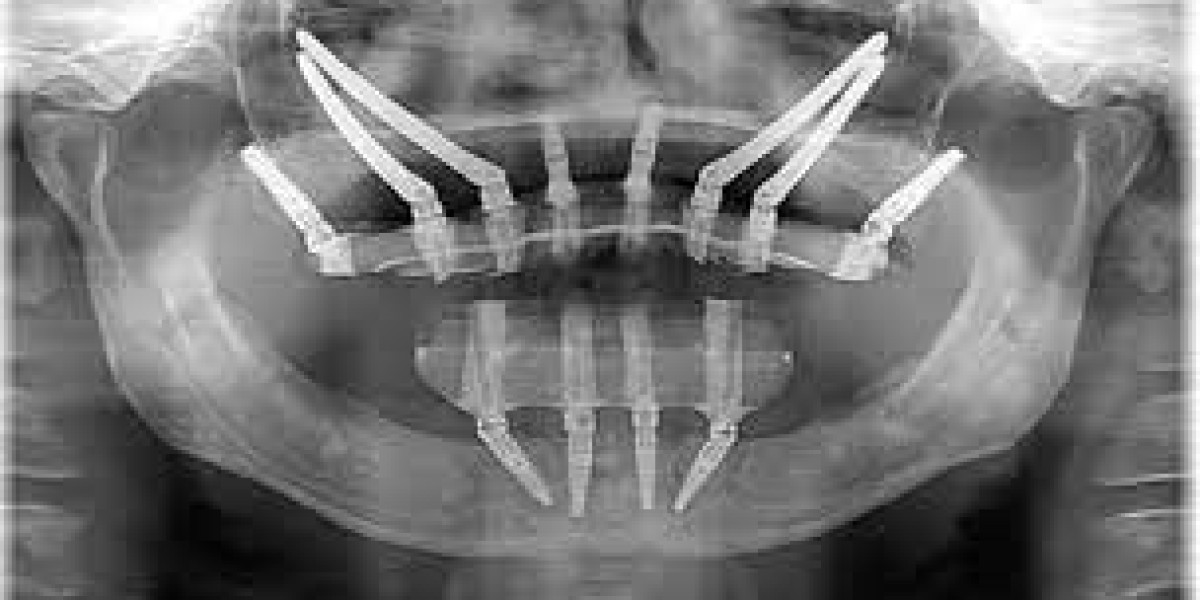
Zygomatic Implants in Dubai, also known as zygoma implants or zygomaticus implants, are a specialized type of dental implant designed for individuals with severe bone loss in the upper jaw. This condition is common among seniors, as bone density naturally decreases with age. Conventional implants require a certain level of bone for stability, making them unsuitable for those with significant bone loss.
Unlike traditional implants, zygomatic implants are anchored in the zygomatic bone, commonly known as the cheekbone. This approach eliminates the need for bone grafting procedures, which can be invasive and carry additional risks for older individuals. Zygomatic implants provide a viable alternative for seniors who may have been deemed ineligible for traditional implants due to insufficient bone volume.
The benefits of zygomatic implants extend beyond their ability to address bone loss. They offer a more efficient and streamlined treatment process, reducing the overall time required for implant placement. This is particularly advantageous for seniors, as shorter procedures minimize potential complications and improve postoperative recovery.
Moreover, zygomatic implants enhance oral function and aesthetics, contributing to a better quality of life for aging individuals. Maintaining proper oral health is crucial for overall well-being, affecting nutrition, speech, and social interactions. Zygomatic implants provide a stable foundation for dental prosthetics, such as dentures or bridges, allowing seniors to enjoy a more natural and comfortable bite.
The psychological impact of dental issues in seniors should not be underestimated. Tooth loss and oral discomfort can lead to decreased self-esteem and social withdrawal. Zygomatic implants address these concerns by offering a reliable and durable solution that restores a more youthful appearance and fosters greater self-confidence in the aging population.
While zygomatic implants represent a significant advancement in dental care for seniors, it is essential to consider factors such as cost and accessibility. As with any innovative medical procedure, the availability of zygomatic implant placement may vary depending on geographic location and financial resources. Healthcare professionals and policymakers must work collaboratively to ensure that this groundbreaking technology becomes more widely accessible to seniors who can benefit from it.
Additionally, ongoing research and development in the field of dental implants are crucial for refining existing techniques and expanding treatment options for the aging population. Advances in materials, surgical techniques, and implant design may further improve the success rates and longevity of zygomatic implants, making them an even more viable option for seniors seeking reliable solutions for their oral health needs.
In conclusion, zygomatic implants represent a transformative approach to addressing the oral health challenges faced by the aging population. By offering a more accessible and efficient solution for individuals with severe bone loss, these implants contribute to improved overall well-being, restoring not only oral function but also the confidence and social interactions of seniors. As the field of dental implantology continues to evolve, it is crucial to prioritize research, accessibility, and education to ensure that seniors around the world can benefit from the latest advancements in oral healthcare.